
When you watch Netflix or Livestream on Facebook, your network needs to have a good rate to load mostly online content without interruption. Others: Listen to online music, download documentation. Some issues can be met easily such as buffering, error downloading, slow loading page time. If your speed is not good enough, the chance of encountering frustrating Internet issues increases. As a result, speed is able to make or break your virtual experience. Most online activities take up internet data, reply on high download speeds. In most situations, the upload bandwidth is smaller than the download bandwidth since most user activities consume the downloading of data from the internet.
Many ISPs have separate bandwidth limitations for downloading and uploading. When understanding and distinguishing speed and bandwidth, users can select the best internet service, internet service provider for their needs. Speed indicates the maximum speed at which digital data is transmitted via a network connection.īandwidth indicates the maximum amount of data that can be transferred from one point to another via your connection in a specific amount of time.ĭiscriminate internet bandwidth and speed Both are measured in Mbps, however, they are still different. speed: What’s the difference?Īnother misunderstanding when it comes to the Internet, they are bandwidth and speed. MBps: Refers to Megabytes per second, which indicates the amount of data is transferred per second. This is a measurement of download and upload speed.

Mbps: Refers to Megabits per second, which indicates how long digital data is transferred. Though interrelated, they are used for different measurements. MBps: What’s the difference?ĭo you know what is the difference between Mbps and MBps? Are they the same?ĭownloading speed is measured in Mbps, however, sometimes, it is misunderstood as MBps.
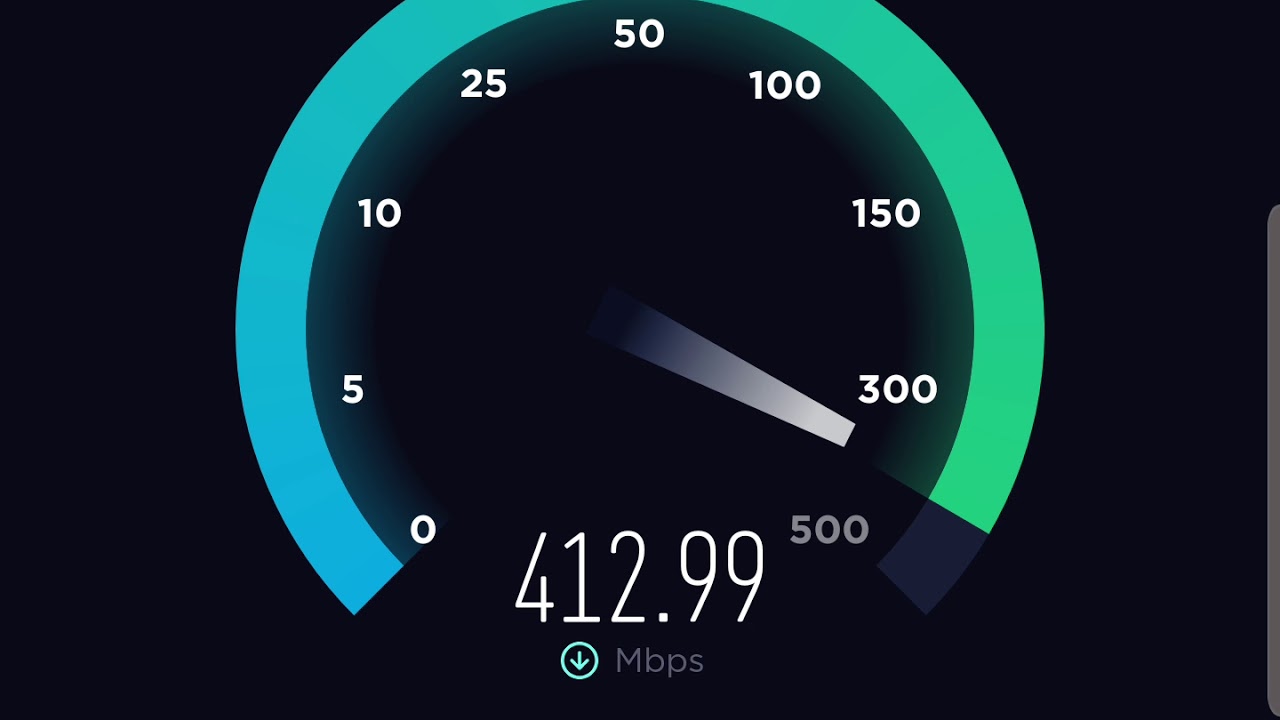
There is a wide range of online activities consuming download data such as watching stream videos, listening to music on Spotify, and downloading files.Īctivities taking up uploading data are live streaming, posting a file/ photo on Facebook, video calls, and sending an email. Whilst, uploading works in the opposite direction, it refers to pushing data from your device to the Internet. The biggest difference between the download speeds and upload speeds is their transferring way.ĭownloading refers to getting digital data from the Internet to your device. That means 1 Mbps ( megabits per second) are 1,000 times quicker than 1 Kbps (Kilobits per second).
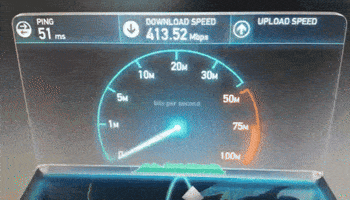
The time is measured in Megabits per second (Mbps).ġ Mb ( megabit) is equal to 1,024 Kb (kilobits). The digital data can be in form of photos, audio, videos, text, files. In most internet speed test, there are 3 main parameters measured: download, upload speed, and ping rate.ĭownload speed refers to how long digital data is taken from the Internet to your device.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
